Posted to News on 8th Jan 2011, 15:59
Draw wire sensors adapted for use inside hydraulic cylinders
Thomas Birchinger, Product Manager for Draw-Wire Sensors at Micro-Epsilon, explains how specially adapted draw wire sensors can be used for measuring the displacement of hydraulic cylinders, thereby avoiding the need to drill piston rods using specialist equipment.
Traditionally there are three different methods of measuring the stroke of hydraulic cylinders. If displacement measurement has already been considered at the design stage, a magnetostrictive sensor can be integrated within the cylinder itself. Alternatively, if the sensor needs to be fitted - or retrofitted - to the outside of the cylinder, draw-wire (string pot) sensors, magnetic or optical measuring rods, or tape measures can be used.
Magnetostrictive sensors are designed so that the measuring element is in a tubular sensor housing - which is always somewhat longer than the respective measuring range. The evaluation electronics are located on or at the base of the cylinder at the rear end of the sensor. For magnetostrictive sensors, a magnet inside the piston is used as the position transmitter.
As these sensors are designed to be pressure-proof, they can be integrated inside the cylinder. Modifying the sensor for the application, by adjusting the bar length, for example, is usually straightforward. However, a bore in the piston rod is required for the sensor tube to be inserted; the greater the stroke of the cylinder, the deeper this bore has to be. In the case of large cylinders, for example in sluice gates, this means that a bore depth of around one metre may be necessary. Vertically boring a cylinder piston in this size range and without tilting is a major challenge.
Rather than an integrated displacement measurement, a draw-wire sensor can be mounted on the outside of the cylinder. This method can be easily achieved, providing measuring ranges of up to a few metres if required. However, in the harsh environments in which hydraulic cylinders are frequently used, the draw-wire sensor can only be used with caution, since dirt and mechanical loads may destroy the sensor over the long term. This limitation also applies if optical or magnetic measuring rods are used. Here, the measuring rod is also installed on the outside of the cylinder. A grid applied to the bar is scanned optically or inductively. As this sensor is also outside on the cylinder, it is susceptible to dirt, dust and soiling.
Due to these limitations, two German companies, Sensor-Technik Wiedemann and Micro-Epsilon, have developed a novel alternative.
Integrated draw-wire sensors

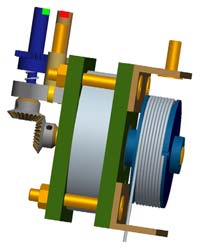
As well as the housing, the critical elements of a conventional draw-wire sensor are the spring, the drum, the measuring wire and the sensing element. A housing for the sensor can be dispensed with in this application, as the cylinder provides this function.
Movement of the piston causes the wire drum to rotate. The rotation is divided using a gearbox onto two shafts with different rotational speeds. A magnet is positioned on each shaft at the bottom of the cylinder, whose positions can be measured by external, magnetic angle sensors. Using a suitable gearbox, each combination of the magnet positions only occurs once across the complete measuring range. The sensor therefore possesses the characteristics of an absolute encoder. Micro-Epsilon was able to contribute much expertise in developing the design of the sensor and function of a draw-wire sensor.
Non-contact signal transmission
Due to the high pressures present, the cylinder walls must be constructed from relatively thick metal. A magnetic signal transmission through these thick walls is not suitable for measurement requirements. Due to Sensor-Technik Wiedemann's experience in pressure measurement technology, a solution to this problem was found without having to weaken the cylinder design. At those points where the two gear shafts reach the bottom of the cylinder, the steel is tapered and a special membrane is welded on. Using this membrane, a magnetic signal can be transmitted with sufficient quality. Using finite element analysis, the minimum possible wall thickness was determined.
The electronics on the outside were designed to be extremely flat and can easily be attached to the bottom of the cylinder. The electronics are available with cabling or connector output. A 4-20mA analogue signal or a CAN interface are also provided as output options.
According to the companies, the system can easily be adapted to different cylinder lengths and diameters and to a diverse range of operating conditions.
Micro-Epsilon's latest wireSENSOR WDS-TZ10 is suitable for cylinders with strokes of 0.5m to 15m. The lubricating oil in the cylinder surrounds the draw-wire sensor; this functions as a lubricant for the sensor, providing a longer service life. This method is also suitable for cylinders without piston rods due to the hooking of the measuring wire. Cylinders with this type of displacement measurement are suitable for use in harsh environments and in mobile construction machinery and off-highway vehicles. For short cylinder strokes, the TZ10 can be used with the magnetostrictive method.
Follow the link for more information about Micro-Epsilon's range of draw-wire displacement sensors.
No. 1 Shorelines Building
Shore Road
CH41 1AU
UNITED KINGDOM
+44 (0)151 355 6070